When choosing a generator for your business, home, or outdoor activities, one of the first decisions you’ll face is whether to opt for a gasoline-powered generator or a diesel-powered one. Both types of generators have their unique advantages, features, and suitable applications. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between gasoline and diesel generators, including their cost, usage experience, power output, and more.
1. Fuel Type and Cost of Operation
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline generators use, as the name suggests, gasoline as their fuel source. Gasoline is typically more readily available and can be cheaper than diesel in certain regions. However, the cost of operation per hour tends to be higher with gasoline-powered generators due to their lower fuel efficiency.
-
10KW Gasoline Generator (Single Cylinder) – China Manufacturer & Supplier for Wholesale$3,800.00
-
5KW series X gasoline engine generator
-
3KW series X gasoline engine generator
-
Portable Silent Inverter Generator – EC2750CZ-B2 & EC3000iS-B2 | Factory Wholesale from China
-
Open Frame Inverter Gasoline Generators | BS3250i-X, BS3750i-X, BS4500i-X | Low Noise & High Efficiency
-
Silent Inverter Gasoline Generator 1.8-3.3KW
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators, on the other hand, are known for their better fuel efficiency. Diesel fuel is more energy-dense than gasoline, meaning that diesel generators can run longer on the same amount of fuel. While diesel fuel can be more expensive than gasoline in some markets, the improved fuel efficiency makes the overall operational cost lower in the long run.
2. Power Output and Efficiency
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline engines generally produce less power compared to their diesel counterparts, which makes them suitable for smaller applications. They are ideal for powering homes, small businesses, or outdoor activities such as camping. Gasoline generators also tend to start quicker and are lighter, making them easy to transport and set up.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are more efficient when it comes to power output, making them the preferred choice for heavy-duty applications, such as construction sites, industrial operations, and large-scale events. They are known for their durability and reliability under extended use, making them ideal for applications where consistent power is needed over a long period.
3. Maintenance and Durability
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline generators tend to require more frequent maintenance than diesel generators. The engine’s components are generally smaller and may wear out faster due to the higher operating speeds of gasoline engines. However, gasoline generators are easier to repair and maintain because of their simpler mechanics.
Diesel Generators
Diesel engines are designed to last longer than gasoline engines, with fewer parts subject to wear. They also require less maintenance over time. That said, diesel generators can be more expensive to repair due to their more complex systems and components.
4. Noise and Vibration
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline-powered generators are generally quieter than diesel generators. This makes them a better choice for residential areas or situations where noise is a concern. However, this lower noise level often comes at the expense of power efficiency and fuel economy.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators tend to be louder and produce more vibration. While this may not be an issue in industrial settings, it could be a drawback in quieter residential or recreational environments. However, modern diesel generators are designed with noise-reduction technologies that minimize these concerns.
5. Environmental Impact
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline engines produce fewer emissions than diesel engines but are generally less efficient in terms of fuel consumption. This inefficiency leads to higher emissions per unit of energy produced.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators, while more efficient, emit higher levels of nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter, which can be harmful to the environment. However, advances in diesel technology and stricter emission regulations are improving the environmental performance of diesel generators.
6. Best Use Cases
Gasoline Generators
- Residential use (homes, small offices)
- Recreational use (camping, outdoor events)
- Small power backup solutions
Diesel Generators
- Industrial and commercial use (construction, mining, factories)
- Large-scale power backup for businesses and hospitals
- Long-duration power supply for remote locations or heavy machinery
7. Pros and Cons
Gasoline Generators Pros
- Lower upfront cost
- Quieter operation
- Ideal for small-scale applications
- Easier to maintain and repair
Gasoline Generators Cons
- Higher operating cost due to lower fuel efficiency
- Shorter lifespan compared to diesel engines
- Less powerful
Diesel Generators Pros
- More fuel-efficient and cost-effective in the long run
- Higher power output, suitable for heavy-duty tasks
- Longer lifespan and greater durability
- Ideal for continuous and large-scale use
Diesel Generators Cons
- Higher initial purchase cost
- Noisier operation
- Requires more complex maintenance
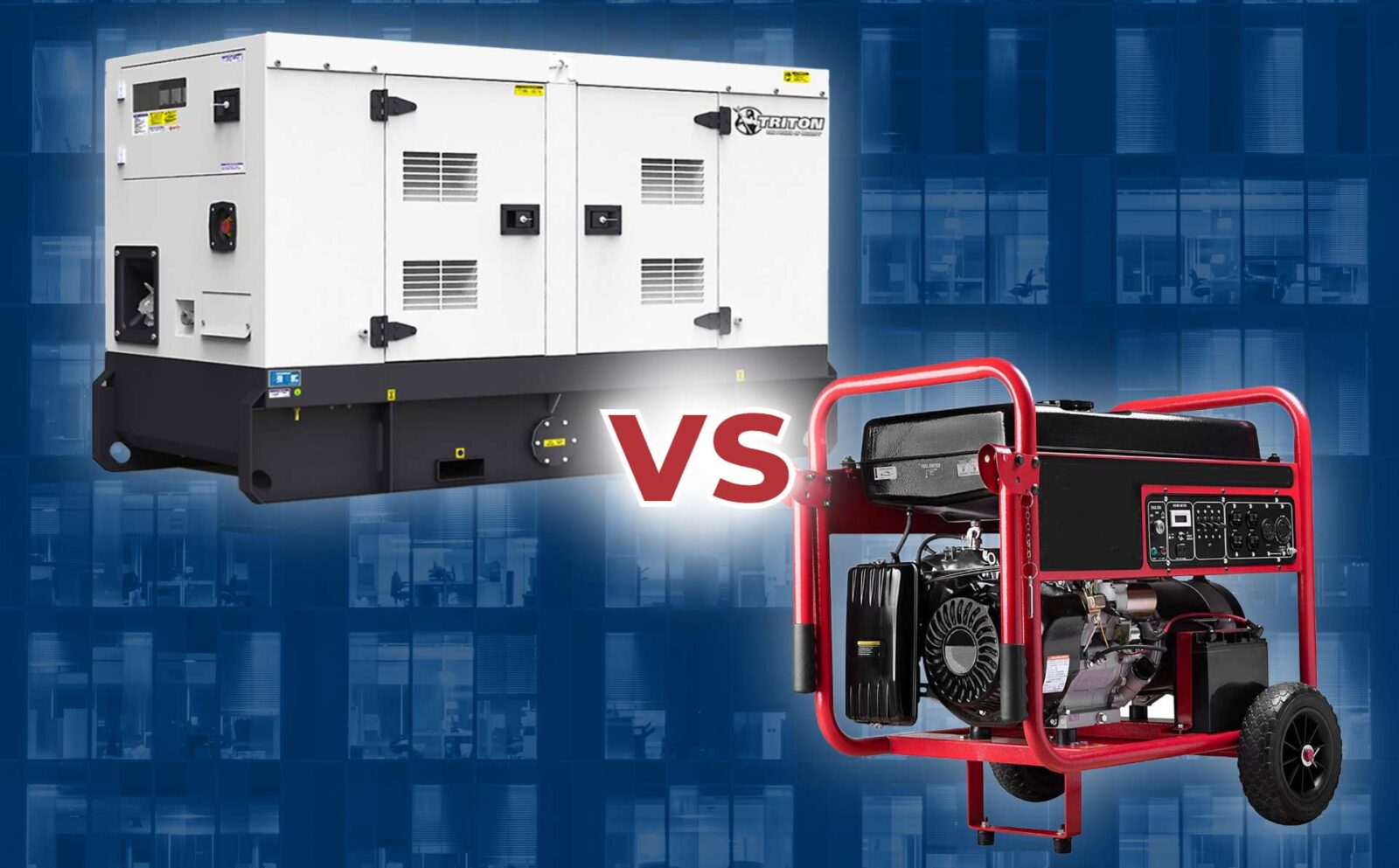
Conclusion
Choosing between a gasoline and a diesel generator depends on your specific needs. If you need a portable, cost-effective solution for short-term or smaller power needs, a gasoline generator may be the right choice. However, if you need a generator for heavy-duty use, requiring long hours of operation and higher power output, a diesel generator would be more suitable due to its efficiency and durability.
At Chinasmallengines.com, we provide a wide selection of high-quality gasoline and diesel generators directly from trusted Chinese manufacturers. Our products are affordable, durable, and ready to serve your needs—whether for residential, industrial, or commercial purposes. We offer competitive prices with global export options, ensuring that you get the best value for your investment. Visit our website to learn more about our generator offerings and make your purchase today!




















